Project Technical Details
APIs / JSON RPC to Implement
🔎 Query API
queryUtxosByAddress: Retrieve UTXOs owned by a specific address within a Hydra Head.queryUtxosByTxIn: Retrieve UTXO information using a specific transaction hash and / or index.queryProtocolParameters: Return hydra protocol parameters used while initializing the hydra node.queryHydraState: Retrieve current state of a Hydra Head (phases include:Idle,Initial,Open,Closed,Fanout).
🏗 Transaction Build API
- Accept JSON-based transaction definitions as input.
- Construct transactions according to Kuber’s transaction specification, modified to work with Hydra protocol parameters.
- Automatically handle fee balancing and validation.
- Support submission and reporting of success or error messages (e.g., invalid transaction structure).
🔁 Hydra Relay API
initializeHead: Start a new Hydra Head.commitUtxos: Add UTXOs to the Hydra Head.decommitUtxos: Withdraw UTXOs from the Hydra Head.closeHead: Signal intent to close the Hydra Head.contestHead: Contest the Hydra Head after closing and before fanout.abortHead: Abort the Head in case of failure or deadlock.fanoutTransaction: Submit the final fanout transaction after Head closure.
These APIs will be exposed as REST endpoints and integrated with a WebSocket backend to provide real-time feedback to users.
Technical Architecture
A draft diagram is available here.
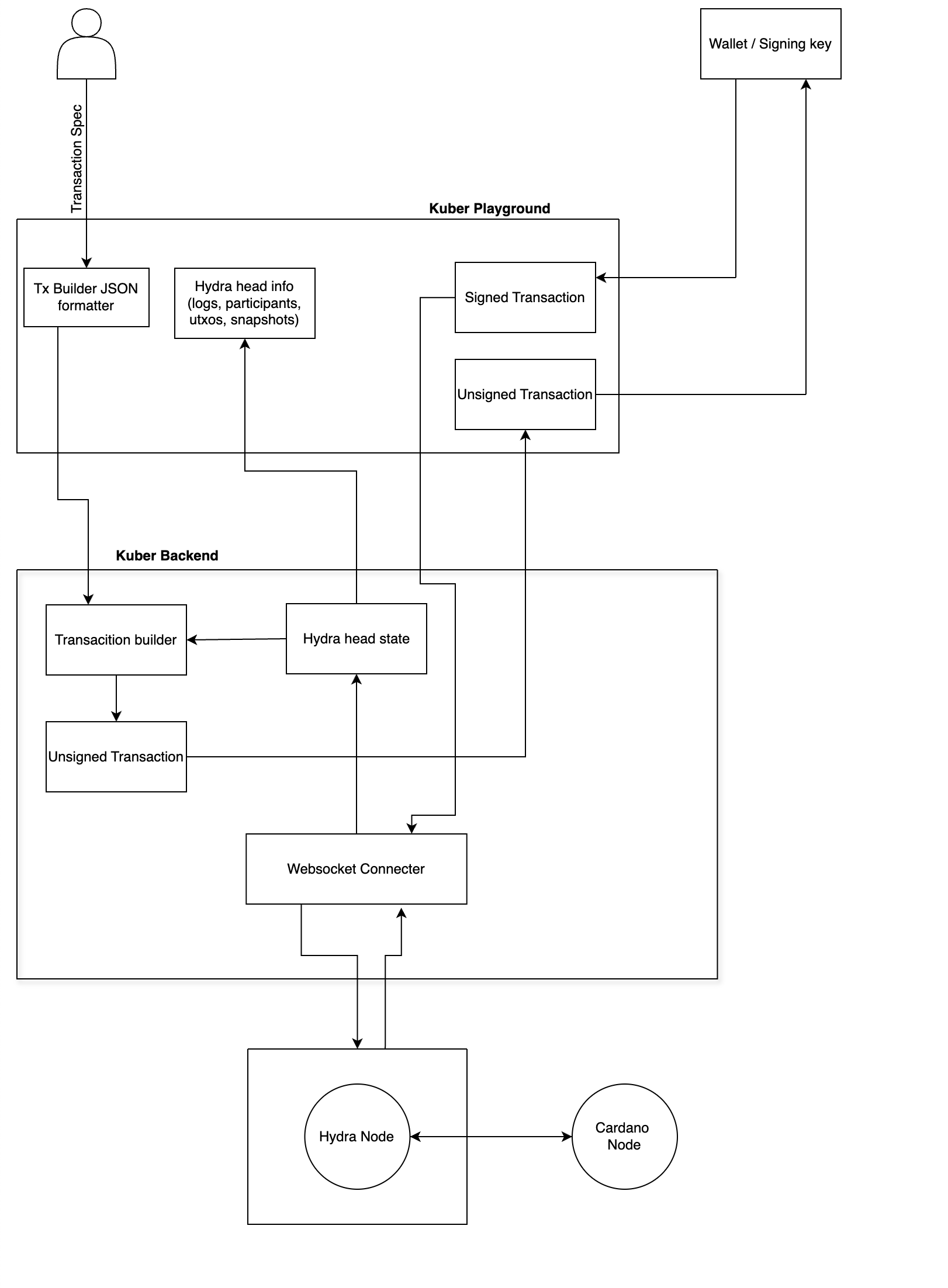
🧭 High-Level Overview
The architecture illustrates how the Kuber backend interfaces with a Hydra node to enable the construction and submission of transactions within a Hydra Head. It also includes developer tooling/ frontend such as the Kuber Playground (Optional), and various internal components for formatting, building, and communicating via WebSocket.
🧱 Components & Flows
1. Playground
- A frontend or client library for experimenting with Kuber APIs. This makes use of kuber-client npm package.
- Construct and Send Transaction JSON (in a Kuber-native-json format) to the backend for processing.
- Connects with browser wallet.
2. Kuber Backend
The heart of the architecture, composed of several interconnected subcomponents:
a. Transaction JSON
- The input from users (via Playground or API calls).
- Defines what UTxOs to use, where to send funds, metadata, etc.
b. JSON Formatter / Tx Builder
- Parses the incoming JSON into a transaction skeleton.
- Constructs a valid unsigned transaction using Hydra’s protocol parameters.
- Ensures all required data (like fee calculation, input/output balancing) is handled automatically.
c. Hydra Head State / Info
- Internally tracked by the backend.
- Includes:
- Current phase (e.g., idle, open, closed)
- Participants
- UTXOs available in the Head
- Snapshots (state of UTXO set at different points)
d. Hydra Head State → Transaction Builder
- The transaction builder consumes the current Hydra head state to determine:
- Which UTXOs are available
- Who the valid participants are
- Which constraints apply to the transaction
This ensures that the transaction being built is valid within the Hydra Head context, not just on Layer 1.
e. Unsigned Transaction
- After JSON processing and validation against the Hydra head state, an unsigned transaction is created and passed downstream for signing.
f. Wallet / Signing Key
- External or embedded component used to sign the transaction.
- May use local signing keys or delegate to an external wallet provider.
g. Signed Transaction
- The completed transaction ready to be submitted to the Hydra node.
3. WebSocket Connector
- A critical module for real-time communication with the Hydra Node.
- Establishes a WebSocket connection using the provided IP and port (configurable by the user).
- Allows:
- Submitting signed transactions
- Receiving real-time Hydra head updates
- Listening to participant activity, state changes, and log events
4. Hydra Node
- A running instance of the Hydra protocol node.
- Works in conjunction with a Cardano Layer 1 node for finality and chain interaction.
- Accepts:
- WebSocket messages for control commands and transaction submission
- Provides:
- Real-time updates on head state, snapshots, participant actions, and UTXO changes
🔄 Key Data Flows
| Source | Destination | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Playground | Kuber Backend | Sends raw transaction request in JSON |
| JSON Formatter | Tx Builder | Converts JSON into internal format for construction |
| Hydra Head State | Tx Builder | Feeds contextual info like UTXOs and participants |
| Tx Builder | Wallet/Signer | Passes unsigned transaction to be signed |
| Wallet | WebSocket Connector | Passes signed transaction for broadcast |
| Kuber WS Connector | Hydra Node | Communicates via WebSocket: transaction submission & state queries/responses |
This architecture supports a fully interactive development and production environment where:
- Users define transactions via a JSON interface (API or playground).
- Kuber formats, validates, and constructs transactions using Hydra context.
- Transactions are signed and submitted over WebSocket to a Hydra node.
- The system maintains a mirrored view of Hydra state and simplifies all interactions for the user.
Components Overview
-
Kuber Server ( Haskell )
- Handles JSON input for transaction requests.
- Builds transactions using Hydra protocol parameters.
- Relays transactions and commands to Hydra nodes.
-
Hydra Node
- Managed by the user.
- Listens for WebSocket commands and responds with state updates.
-
Kuber WebSocket Proxy
- Connects to the Hydra node WebSocket.
- Translates and structures messages into Kuber-native JSON.
- Enables clients to subscribe to transaction statuses and state updates.